Smart contracts are the backbone of decentralized finance. Through smart contracts, users can interact with dApps without middlemen. Blockchain design has a significant impact on the capabilities of smart contracts. Ergo Blockchain’s UTXO model allows multi-stage contracts to operate on a highly scalable network.
Decentralized Finance
The banking system is built solely on trust. However, this trust mechanism is a form of obligation that citizens don’t have any choice on. Banks and financial institutions produce and provide financial products such as loans or ETFs to financial markets. The value of these products is defined by what they are referring to as an actual asset, either a physical object or a contract. The credibility of value, however, is protected with our blind trust in these institutions. Governments back up these financial institutions to restore confidence, but to what degree are they trustable?
The problem lies elsewhere. We don’t ask if our stock is genuine or is it a fake duplicated one. Everything is working on a digital database, and we can see whether it is real. We can see our money in our bank account, but still, it doesn’t mean that it’s real. The modern monetary system works on a fractional banking system, so we know that only about 10% of the money in circulation is real money. We continue trusting financial institutions as if they hold some collateral against our money in banks. However, as we can see in history, during “banking panic runs” or “debt crises”, it’s not easy to control a vast financial system and foresee these kinds of unexpected events. The outcome of this then usually affects the personal users rather than big institutions.
Smart contracts are therefore built for this, to let you know where your money is at all times. Whatever application you use, if smart contracts govern it, then you know how your funds are secure. That’s the beauty of a non-custodial financial system; you don’t have to give your funds to a financial institution to use their services. You can use a variety of financial services without giving up custody of your funds. You don’t have to pay abrupt fees to your bank to secure your funds. Not only that, but you can even make money using smart contracts by taking initiatives such as lending your funds or providing liquidity to markets. These are the strategies that blockchain envisions in a decentralized, peer-oriented, secure, and accessible financial system.
Multi-Stage Contracts On Ergo
So you’ve heard about smart contracts, but what are multi-stage contracts? Multi-stage contracts refer to smart contracts that are operating on a stateful level. Because Ergo uses the UTXO model (first seen in Bitcoin), it is possible to process parallelized actions on top of smart contracts. Ethereum’s Account-Based model, however, doesn’t allow such operations. The Account-Based model has its ease of use, but it also comes with a high load of operation power. Ergo’s multi-stage contracts are developed on the extended UTXO model. It’s a complex design that aims for infinite scalability; therefore, it creates more place to build complex solutions.
For a blockchain to contain smart contracts, it should have loops. These loops can later refer to themselves and check whether an operation is working or not. Bitcoin’s UTXO design is very primitive, and it doesn’t contain Turing-complete smart contracts. Ethereum has this capability, but it’s a primitive version of a Turing-complete language. Ergo Blockchain provides a different approach to multi-stage contracts, empowered by the extended UTXO model. Permitting a lighter network and broader use cases.
Use Cases of Ergo
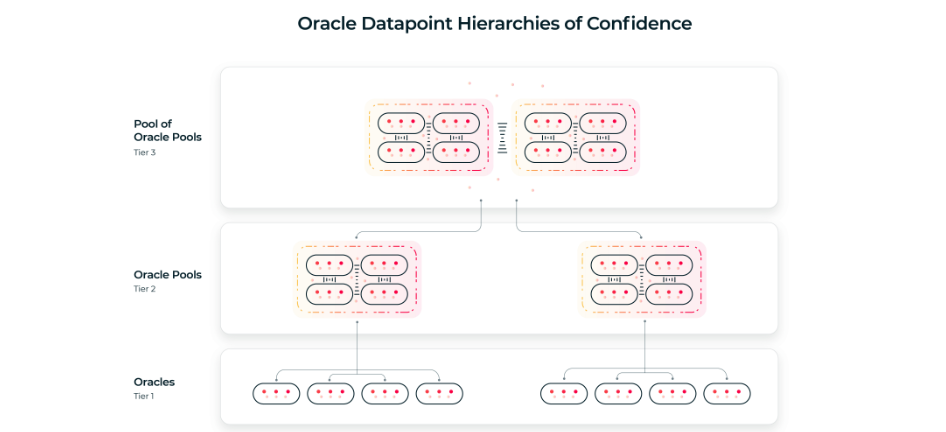
Oracles: Oracles are the messengers in and out of blockchains. They contain valuable data (e.g. price feed) so that applications work seamlessly. Ergo Blockchain’s design allows Oracle Pools, and this would help to create data hierarchies. A system of oracles that can be scored regarding their trust level is a significant phenomenon. Chainlink’s oracles aren’t capable of forming oracle pools because it’s built on the Ethereum network. Yet Chainlink recently published a whitepaper about decentralized computational networks interacting with blockchains, an idea that Ergo already working on with oracle pools.
NIPoPoWs: Non-interactive proofs of proof of works can be used to build an interoperable blockchain ecosystem. With NIPoPoW implementation, Ergo Blockchain can interact with the smart contracts on proof of stake networks. This would open up an integrated use case between different dApps on different blockchains. Cardano is already planning to implement side chains with NIPoPoWs in collaboration with EMURGO. Limits are yet to be discovered.
Multi-Sig: Multi-Sig or Multi Provers are helpful for the reliability of smart contracts. This kind of implementation is vital for security. So that smart contracts aren’t in control of one person, but rather governed by multiple accounts. Multi-stage contracts can also be designed for punishing malicious actors trying to take control of smart contracts.
Time Epoch: Ergo Blockchain can be designed to have timed operations. For example, during an ICO (or IDO), a code in a smart contract can provide timed release so that investors have a protective layer if the project owner isn’t delivering his/her promises. In Ethereum, programming such a kind of timed operation isn’t possible.
Parachain/Sidechains: This is a yet-to-develop area for Ergo Blockchain. It’s certainly possible, and we know that the implementation of parachains has a significant impact on scalability. Our core developer Alex Chepurnoy is about to release a paper on it, so stay tuned!
Sources:
https://ergoplatform.org/docs/teaser.pdf
https://ergoplatform.org/docs/ErgoScript.pdf
Multi-Stage Contracts in the UTXO Model: Delivery by Alexander Chepurnoy & Amitabh Saxena